SCADA system have been widely accepted in the business world. This is due to perform repetitive processes automatically and thus achieve profitability in production times.
Today, the industry requires more homogeneous products, and fewer operators, as they are not part of the production process as such. Their tasks now consist more of supervising the correct operation of the machines. The aim is to control, at all times, the machines involved in the production process and to collect real-time data on the processes.
Rise and growth of automated systems in industry
The evolution of these processes has increased at a dizzying pace. From its beginnings to the present day, it has taken giant steps forward, thanks to the continuous improvement of control and data acquisition devices, which are increasingly faster, more reliable and easier to intercommunicate with other devices.
Process control requires devices to be increasingly versatile and interconnectable with each other. The basic aim is to collect more information to be able to detect irregularities, temperatures, running times, fault histories, etc.
To be able to act, control and supervise these processes, visualization environments are programmed. These will be shown to the operators who will be in continuous contact with the Scada, which will provide them with information about the machines. Thus, they will be able to make changes in the values of each machine: temperatures, motor status, alarms, etc..
MG Electricidad stands out for being a company specialized in SCADA systems, a vital tool in industrial automation, which in our case we implement mainly in the food industry. However, in recent years its use has spread in all types of sectors, such as pharmaceuticals, energy, manufacturing and assembly lines of machinery and / or food, etc..
SCADA: elements and benefits
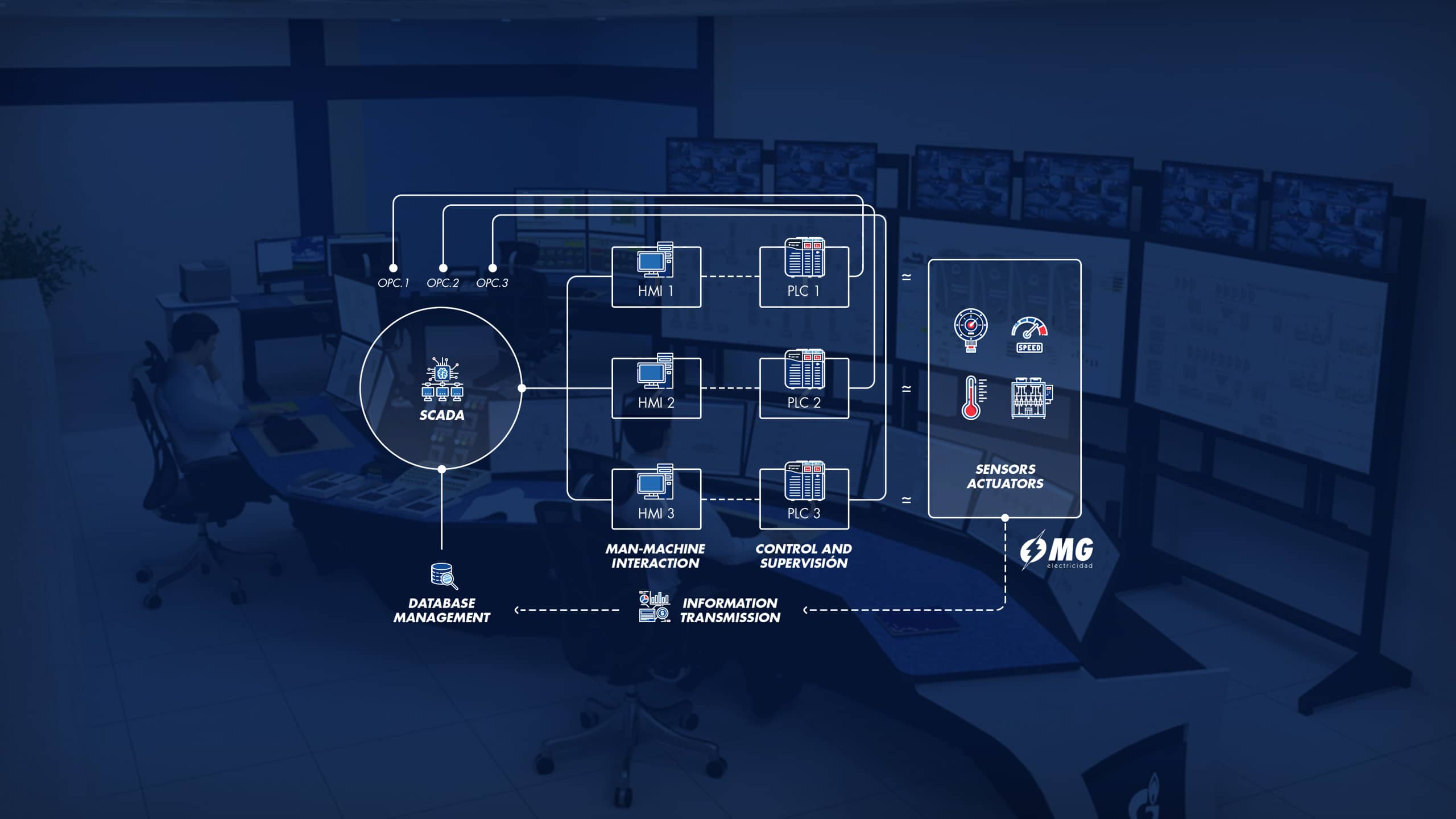
What is a SCADA system
The SCADA (Supervisory, Control and Data Acquisition) system is a versatile tool that adapts to the needs of each type of installation and/or process to be automated.
It is a set of intercommunicated computer applications and programs to act and receive information from the various actuators and sensors that have been implemented throughout the line and / or machine to be automated. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a visual environment as functional and intuitive as possible for the continuous handling of the information that it will have to perform throughout its useful life. This will be installed in a computer that can be at the machine (considered as HMI) or far from it (considered as Scada), and thus be able to control the production process at all times.
The main structure of a SCADA system is composed of programmable logic controllers (PLC) and remote terminal units (HMI)
PLCs are responsible for managing and/or controlling the sensors and actuators involved in the installation. They are the real brains of the installation, since they are the ones that activate or deactivate the elements as they have been initially programmed; that is to say that if a certain input is told that it is a failure signal and this is activated, the PLC recognizes it and makes, for example, a motor stop and also activates an alarm to warn that a failure has occurred in that motor.
HMI: Visual Process Control
The HMI are the visual environments in which the operators interact with the lines and machines to be controlled. They are the screens with programmed interfaces to visualize the data received from the PLC. In these screens you can see the “PV” (actual value) and the “Set Point or desired set point” (value at which we want to work a particular machine or motor). These are integrated by microprocessors that communicate with each other by means of certain communication protocols.
The HMIs will be distributed at different strategic points, for greater manageability when controlling the entire production line. The devices in charge of capturing information from the environment are called sensors: temperature probes, level probes, load cells, etc. And the so-called actuators are those that are responsible for performing certain actions when necessary. We can find solenoid valves, pistons, motors, etc.
Automation and control
With the help of sensors and actuators, necessary for the process to be automated, we will be able to control remotely and/or at the machine, both individual machines and entire production lines. In turn, with the data collected throughout the process, we can control, monitor and above all, perform an analysis to make decisions regarding future improvements. In short, correcting and polishing errors thanks to process automation.
Basically, SCADA systems are software programs installed on a piece of equipment, usually a computer, that meets specific requirements for which it has been configured in order to control the production process in an automated way.
How a SCADA and/or HMI system works
After an action and condition foreseen in a production line, the PLC directs and manages the information to the computer with SCADA and/or HMI software. It processes, distributes and displays the data to the operator or maintenance technician. Ultimately, by viewing the values in real time, the operator will analyze and make decisions on the fly.
For example, the SCADA and/or HMI system will instantly notify the failure of any motor, activating an audible or visual alarm. After the warning, the operator will stop the alarm and will be able to see which engine is causing the problem. With this, maintenance work and speed in solving them are facilitated.
The capacity of the SCADA and/or HMI system lies in notifying and providing constant information to technicians about errors and what conditions the production is in at any moment (for example: temperatures, weights, processed parts, etc.). With the information you provide us, you help us to resolve current and future faults more quickly. Since, if we observe that these failures are persistent, we can plan improvements and/or calculate the useful life of the material, and thus change it before it becomes a problem for production.
What SCADA software can do
The SCADA system is composed of different software elements to facilitate the control process, including automatic processes that produce the following functions:
- Control and supervision of the systems that make up the automated production plant.
- Acquisition of data of the elements that have been integrated in the installation.
- Elaboration of reports for later analysis together with the previous data.
- Recording of incidences, with an alarm system.
- Performing complex arithmetic calculations for the realization of self-adjustments (e.g. servo motor, solenoid valves, positioning pistons, etc.).
- History and/or data collection from remote systems.
- HMI interface: visual control panel to facilitate communication between user and machine.
- Internal and external communication with any computer with the appropriate software for this purpose.
- Quality control over plant production.
- Open and flexible architecture for possible future improvements and upgrades.
SCADA elements
Human machine interface (HMI)
Mostly graphical environment, which facilitates the interaction of the user with the machine. This is usually located at the foot of the machine to be controlled. Its function is to show and let the operator change the process data by means of a previously programmed system. Its purpose is that the operator has the maximum information at all times and in the most intuitive way.
Programmable logic controller (PLC)
Commonly referred to as programmable controllers, these are used in the system as field devices because they are responsible for collecting information from the devices that make up the installation, processing it and executing the processes to which they have been pre-programmed (it could be said that it is the real controller of the line).
Supervisory control and acquisition (SCDA)
Mostly graphical environment, which facilitates the user’s interaction with the machine. Usually, the user will be away from the machine, so the control will be carried out from an independent room. Its function will be to show and let modify the process data to the operator by means of a previously programmed system. The purpose, to give information at every moment in the most intuitive way.
Network or communication system
It is responsible for establishing communications with the various devices that make up the installation and thus to ensure that there is a fluid and continuous communication of information.
Sensors
These are devices that act as detectors of physical or chemical quantities, called instrumentation variables, and convert them into electrical variables or signals for possible interpretation and management of these in the production process (e.g. product temperatures, silo levels, etc.).
Actuator
Mechanical device used to act or provide movement on another mechanical device in order to control and/or manage the elements involved in production, e.g.: solenoid valve, piston, etc.
Benefits of SCADA and/or HMI system
In MG Electricidad we believe in our work faithfully, that is why we emphasize the importance of SCADA systems in industrial automation. A SCADA system allows an industry to study the steps it wants to achieve. In that way, anticipate the appropriate response to the conditions indicated and execute certain actions automatically in an efficient way.
We are talking about programmed conditionals, cause-consequence automations that facilitate the mechanization of processes that, if carried out manually, would be deficient and practically impossible to cover.
Examples of SCADA
A clear example of these automation systems is the realization of electrical panels tailored to the needs of each customer. Since each customer has specific needs. In MG Electricidad we advise and shape their projects through the design, installation and subsequent programming of the elements that integrate the process to automate.
Most of our customers are in the food industry. The processes that we usually automate in this area are cleaning, peeling, roasting and transformation of nuts into other derivatives such as flours, rolled products, etc.
Efficiency and productivity
In short, we can eliminate human errors through SCADA systems, since it allows us to visualize and precisely control the machine and thus be able to monitor the equipment and processes that are being performed in real time. The aim is to automate the most common and repetitive tasks that were previously performed by one or more operators.
In any industry, there is a point of growth where the implementation of a SCADA system becomes necessary. Its use will allow remote monitoring and control of a machine, where a company may lack the necessary manpower. Thus, faithful communication and operability of such tasks is vital for profitability and economic survival.
MG Electricidad SCADA Solutions
MG Electricidad distributes, configures and adapts different SCADA software solutions with SIEMENS technology, and other industrial software distributors. We work based on the needs of each production plant, to provide the most versatile and flexible SCADA solution.














