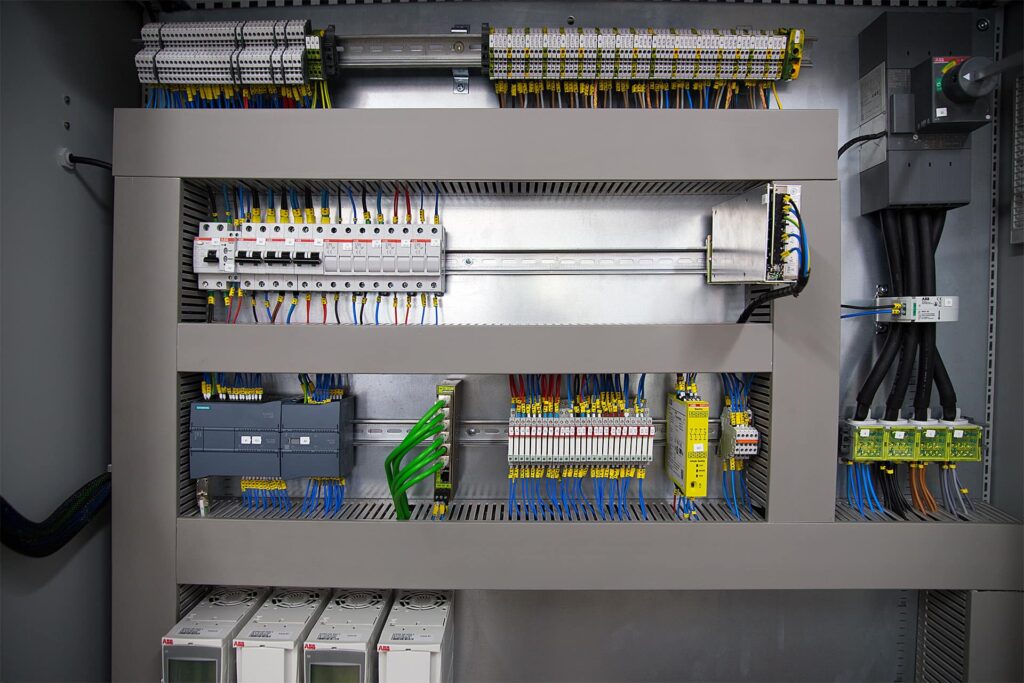
One of the main services we offer to companies is the automation of industrial processes. In MG Electricidad we work mostly in the food industry sector, although we also cover other disciplines such as graphic, pharmaceutical, chemical, oil, plastic, telecommunications. Lets talk about advantages of industrial process automation.
We believe in automation as a key issue for companies in all types of industries. In the kind of global marketplace we find ourselves in, the evolution and survival of many industries can derive from any production advantage they may have over their direct competitors.
Competitiveness and the nature of the selection between supply and demand, urges us to be increasingly profitable and efficient in our type of production, and the automation of industrial processes will help us achieve the maximum optimization of time and costs.
Industrial Process Automation Concept
Industrial automation is the use of technologies for the control and monitoring of industrial processes, devices or machinery, which usually represent serial functions, making certain actions work automatically, reducing human intervention in the development.
Automation in turn allows us to implement innovative solutions, which on balance improve old manual processes. Implementation of technology and control systems, such as software, electrical panels, circuits or communication centers, for the management of machinery and production lines.
For example, automation for processing separation and cleaning in the nut food industry has improved product quality as well as increased product quantity with the use of less energy and manpower.
The automation of industrial processes gives us the ability to manage and control each phase of business. In MG Electricidad we study the most efficient solution, depending on your company, and if it requires complex but repetitive operations, where it is also necessary a high level of safety and accuracy in the execution of each operation.
Automation of industrial processes

Industrial automation environments
There are two environments where industrial automation is applicable: OT environments or operational environments, where traditional manufacturing tasks are carried out; and IT environments or information environments, focused on computers and their software system.
That is, the operational part are elements such as sensors, actuators, cylinders, motors, cells, vision systems or pneumatic compressors, which make a robot or machine can develop a particular task. While the second part deals with these physical elements by means of a programmable logic controller, API, PLC or automation stations.
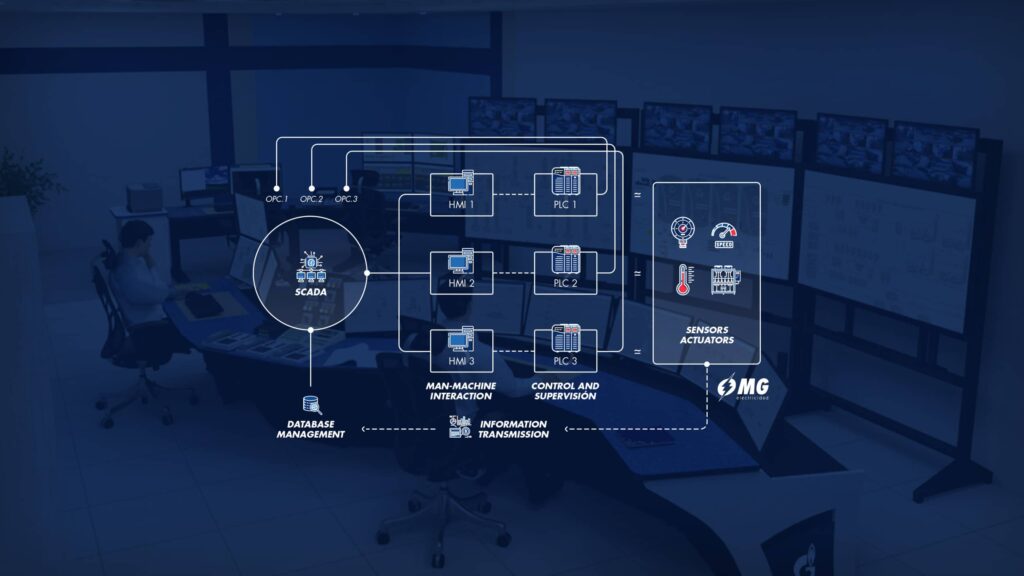
Within the application environment, MG Electricidad stands out in certain control software, such as supervisory control and data acquisition systems (SCADA) or management software such as MES or ERP. In reference to industrial automation in IT environments, one of the latest trends in the sector is RPA (Robotic Process Automation) technology, which offers the replacement of manual tasks by automated tasks without modifying the order of the processes.
An automated system uses various special hardware and software elements and components to implement control and monitoring systems. In recent years, the number of these products has developed from various suppliers who market their own specialized products. At MG Electricidad we work with several of these suppliers, such as ABB, Ifm, Rockell Automation, Rittal, Sick, Eldon, Siemens, among others.
Types of industrial automation
Fixed industrial automation:
- Fixed industrial automation. Relatively simple and affordable mechanization systems, configured for specific tasks. On the downside, if such activity is no longer necessary, they cannot be used for another task. Still, they are often the best choice when we are looking to produce very high volumes of a given item at the highest possible rate.
Programmable industrial automation
- Capital for the production of various types of products in batches. They are usually slower than fixed systems, although their configuration is more versatile and adaptable to production needs.
Flexible industrial automation
- These systems combine the benefits of fixed and programmable technology: the production rate is similar to fixed industrial automation, while providing scope for setting alterations throughout the process.
Industrial automation equipment or tools
The following is a summary of the equipment or elements that perform certain industrial automation functions, such as control, detection, supervision and monitoring.
Sensors and actuators
Sensors transform physical process variables such as flow, pressure or temperature into electrical or pneumatic variables. Their signals will be used to process information, analyze it and, based on that, make decisions to produce the control output.
Finally, the controllers produce the calculated outputs and are applied as inputs of electrical or pneumatic signals to the so-called actuators, which will convert the electrical or pneumatic signals into physical variables of the analyzed process. Among the actuators we can find elements such as relays, control valves, motors…
Apart from the above systems, there are the so-called intelligent instruments: integrated systems for detection or actuation of elements, which stand out for being able to establish communication with the field buses. Such devices are composed of an internal signal conditioning circuit and allow a direct connection to the communication link in the industrial bus system.
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
The programmable logic controller (PLC) is a capital device of industrial automation. It is a programmable logic controller, which allows you to control the devices and change easily from one process to another. The PLC is intended for multiple input and output configurations and is capable of withstanding high temperatures with resistance to vibration and shock.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
SCADA is an application that captures operating data from the system in order to control and optimize it. Applications can be the actions of a petrochemical distillation process, a pipeline compressor, or a water filtration system…
The existence and evolution of any company, regardless of the sector to which it belongs, is due to the need to optimize the performance of its assets through operational excellence. Staying ahead of the competition allows you to find more agile workflows with less effort.
Human Machine Interface (HMI)
The Human-Machine Interface (HMI) incorporates an electronic system necessary to indicate and control the status of industrial automation equipment. In addition, it helps us control industrial automation equipment.
Artificial Neural Network
This system is based on a mathematical model and is responsible for processing the information that arrives from the communication networks. ANN structures can be changed based on certain external and internal data entered in the system configuration phase.
Distributed Control System (DCS)
The Distributed Control System (DCS) is another industrial automation system, very popular for its use in multiple processes within the manufacturing industry. Its different applications include electrical power networks and generation plants, environmental control systems, traffic signals, water management systems, chemical plants, manufacturing and classification of pharmaceutical products, among others.
Robotics
Parallel to the evolution of technology, the use of robotics has become normalized in different industrial fields. Robots can be helpful in carrying out various application tasks like mapping, painting, welding, repairing, etc. The role of industrial robotic systems during the production process encompasses everything from the beginning of assembly and internal treatments to the final tests of said process.
Advantages of industrial process automation
Currently, many companies are aware of the importance of introducing new generation industrial automation systems in the workplace. However, many are not active in such an implementation, knowing that automating processes will be essential sooner or later to maintain their level of competitiveness in the future. Next, we describe the advantages of automating industrial processes:
- Reduction of manufacturing costs.
Industrial automation systems are very cost-effective in terms of return on investment. They operate only with maintenance costs that can be planned and perform activities that would otherwise require a lot of manpower. - Increased efficiency of the production process.
Industrial systems are essential when carrying out repetitive tasks and once configured and calibrated they do not modify their operation, that is, they always have consistent results. - Fast processing of all production information.
Machines that automate processes in industries are significant because of their ability to work endlessly. - Agility in responding to market demands.
The accelerated increase in demand for food production globally has driven the automation of industrial processes. There are many companies in the food industry that are adopting automated systems to reduce labor burden and grow business at a respectable pace.
Improving process safety and production quality.
By reducing costs associated with the implementation of these systems, it is possible to offer more products, of better quality and at better prices.
More accuracy in quality controls.
The quality/price ratio is the biggest dilemma among food producers and consumers. The use of automated machinery for processing and packaging products makes it possible to monitor and correct defects conveniently.
Control of all processes.
Automation allows us to track products through their processing and distribution stages. In this way, we can simultaneously ensure quality, safety and profitability. In addition, if a defective batch of product is found, we can separate it as quickly as possible.
Remote repair.
Repair, maintenance and retrofitting of robotic systems and electric motors can be carried out remotely by automation technicians.
Efficient use of energy and raw materials used for the product:
Industrial automation optimizes the use of materials, thus avoiding wastage of raw materials, with robot arms being more efficient than human arms in almost all lines..
Flexible and scalable production.
Flexibility and expandability are two great advantages of industrial process automation. Although it is not easy for small companies to opt for a complete integral automation solution, they can add components and machinery based on their needs, and thus expand their business in a scalable way.
Automation is the future
In short, automation is key to Industry 4.0 and can now be considered a must-have value among industrial companies. According to Fortune Business Insights, the industrial automation market is expected to grow by 200% by 2026. For all these reasons, automation represents advantages in many aspects, but first and foremost in terms of time and cost savings.